
VOApplication: an XML Encoding Schema for Application Resource Metadata
Version 0.9
IVOA Working Draft 20 April, 2011
- This version:
-
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/WD/ReR/VOApplication-XXXX.html
- Latest version:
-
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/latest/VOApplication.html
- Previous versions
-
- Authors:
-
Paul Harrison, Editor
and the IVOA Registry Working Group.
This document describes an XML encoding standard for IVOA Application
Metadata, referred to as VOApplication. This schema is primarily
intended to support interoperable registries used for discovering
resources; however, any application that needs to describe resources
may use this schema. In this document, we define the types and
elements that make up the schema as representations of metadata terms
defined in the IVOA standard, Resource Metadata for the Virtual
Observatory [
RM]. We also
describe the general model for the schema and explain how it may be
extended to add new metadata terms and describe more specific types of
resources.
This is an IVOA Working Draft for review by IVOA members and other
interested parties. It is a draft document and may be updated,
replaced, or obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is
inappropriate to use IVOA Working Drafts as reference materials or to
cite them as other than "work in progress."
Parts that the editor considers should be removed from the document are marked in red with a strike through line, and parts to be expanded are in green
Comments on this document are now welcome for consideration in the next version of this
document. They should be sent to
registry@ivoa.net,
a mailing list with a
public
archive or on the
VOApplication
twiki discussion page. General discussion of related technology is
also welcome on the
Registry WG
wiki site.
A list of current IVOA
Recommendations and other technical documents can be found at
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/.
This document has been developed with support from the
National Science Foundation's
Information Technology Research Program under Cooperative Agreement
AST0122449 with The Johns Hopkins University, from the
UK Particle Physics and Astronomy
Research Council (PPARC), and from the
European Commission's Sixth
Framework Program via the
Optical Infrared Coordination Network (OPTICON).
Conformance-related definitions
The words "MUST", "SHALL", "SHOULD", "MAY", "RECOMMENDED", and
"OPTIONAL" (in upper or lower case) used in this document are to be
interpreted as described in IETF standard, RFC 2119
[RFC 2119].
The Virtual Observatory (VO) is
general term for a collection of federated resources that can be used
to conduct astronomical research, education, and outreach.
The International
Virtual Observatory Alliance (IVOA) is a global
collaboration of separately funded projects to develop standards and
infrastructure that enable VO applications.
XML document validation is a
software process that checks that an XML document is not only
well-formed XML but also conforms to the syntax rules defined by the
applicable schema. Typically, when the schema is defined by one or more
XML Schema [Schema] documents (see
next section), validation refers to checking for
conformance to the syntax described in those Schema documents. This
document describes additional syntax constraints that cannot be
enforced solely by the rules of XML Schema; thus, in this document,
use of the term validation includes the extra checks that goes beyond
common Schema-aware parsers to ensure conformance with this
document.
Syntax Notation Using XML Schema
The eXtensible Markup Language, or XML, is document syntax for marking
textual information with named tags and is defined by the
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Recommendation,
XML 1.0
[XML]. The set of XML tag names and the syntax
rules for their use is referred to as the document schema. One way to
formally define a schema for XML documents is using the W3C standard
known as XML Schema [Schema].
This document defines the VOApplication schema using XML Schema. The
full Schema document is listed in Appendix A.
Parts of the schema appear within the main sections of this document;
however, documentation nodes have been left out for the sake of brevity.
Reference to specific elements and types defined in the VOApplication
schema include the namespaces prefix, va, as in
va:Application (a type defined in the VOApplication schema).
Use of the specific va prefix in compliant instance documents is
not required (the namespace could be assigned to any prefix); its use in this
document is simply to indicate that it is an entity defined in the
VOApplication schema.
Namespace prefixes used in this document
| prefix | namespace |
|---|
| vr | http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOResource/v1.0 |
| vs | http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VODataService/v1.0 |
| va | http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOApplication/v1.0 |
1. Introduction
The IVOA Standard,
Resource Metadata for the Virtual Observatory
[Hanisch et al. 2004] (hereafter referred to as
RM) defines metadata terms for describing resources.
A specific XML encoding of these resources is described in the IVOA standard VOResource: an XML Encoding Schema for Resource Metadata [Plante et al. 2006] (hereafter refered to as the VR) The "resource" that is described in these documents is a very general concept, and was deliberately designed so that it can be specialized for particular types of resource.
This document specifically describes an extension of the metadata concepts and an XML encoding called
VOApplication. The VOApplication schema provides XML encoding that extends the VR so that can be used to describe applications (see section below for discussion of what constitues an application). The intention of creating this model is to allow a framework for finding applications in an IVOA compliant registry and possibly downloading and automatically running them.
1.1. Related IVOA Standards
2. The VOApplication Data Model
The concept of an application in the context of this standard can cover almost any computer program or process than can consume and/or emit data. e.g.
- unix command line executables
- java applets
- REST web services
- SOAP web services
Note that although this is a very wide ranging definition, forms of "application" e.g. web services which are specifically covered by other IVOA standards, should normally be described in terms of those standards, rather than as a general VOApplication.
2.1. Core VOApplication Metadata
At the IVOA interoperability meeting in Madrid 2005 a list of desired metadata for applications was agreed.
- Function
- A delimited list, including terms such as reduction, analysis, display, modeling,
graphics, format conversion, etc. Multiple terms could be selected.
- OperationModes
- Interactive, command line, scriptable, from browser, etc.
- OpenSource
- Yes/No.
- SourceURL
- Entry point to the source code.
- License
- Name of license and descriptive text.
- Cost
- Free; or description of pricing, if not freely available.
- SourceLanguage
- A delimited list of software development languages. Can be more than one.
- Dependencies
- A text description of dependencies � compilers, libraries, etc. � that this
application needs in order to be compiled or deployed. Include IDs of other
applications in the registry upon which this application relies.
- NetworkRequired
- Essential/Useful/Limited/Unnecessary.
- BinarySize
- Typical size of the executable.
- MemorySize
- Typical memory requirements.
- Platforms
- List of supported platforms (hardware plus operating system).
- VOStandards
- List of supported VO standards and protocols used or implemented in this
application (SIAP, SSAP, ADQL, OSQ, etc.)
- InputFormats
- List of supported input data formats, e.g., FITS, HDF, VOTable.
- OutputFormats
- List of supported output data formats, e.g., FITS, HDF, VOTable.
- Appliction Version
- It is often the case that applications are updated - not clear that the version element that appears in curation is sufficient for the needs (how is the latest version of an application signalled, if access to legacy versions are left in the registry.
Note that this model does not attempt to categorize the function of the application - this is beyond the scope of this standard, and will be covered by either the IVOA Semantics WG efforts, or by the characterization of processes that is being undertaken by the IVOA Theory WG. The only characterization of the application in this model is in terms of the types of inputs or IVOA standards that it supports.
2.2. Formal UML model
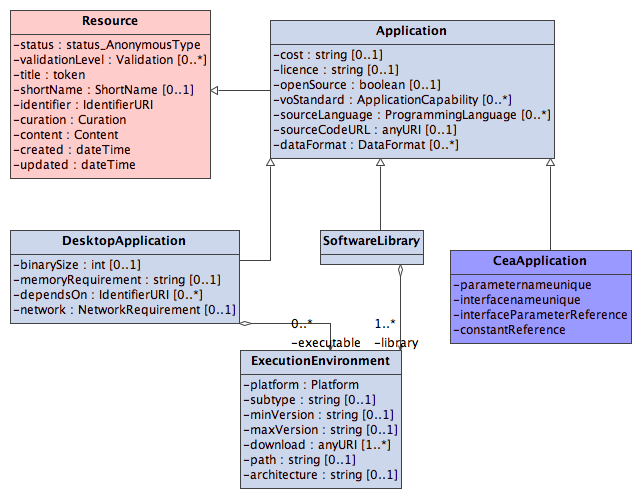
The main type introduced by this specification is the va:Application which contains all of the generic application metadata. The main subcategorizations of an application are then;
- Desktop Application
- An application that can be executed locally by a user on their desktop machine and is represented by the va:DesktopApplication type.
- Software Library
- A collection of software that is not directly executable itself, but can be used to build other applications - represented by the va:SoftwareLibrary type.
- Remote Application
- An application that is executed remotely from the users desktop. There is no specific type defined for this class of application in this VOApplication schema, but this class of application is represented in the diagram above by the CeaApplication type which is defined in a separate schema [CEA]
3. Details of the VOApplication Schema
3.2. Application Type
This is the basic extension to the VOResource type that this schema defines. It is the container for the basic metadata that are common to all applications.
<xs:complexType name="Application" >
<xs:complexContent >
<xs:extension base="vr:Resource" >
<xs:sequence >
<xs:element name="cost" minOccurs="0" type="xs:string" />
<xs:element name="licence" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="openSource" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="dataFormat" type="DataFormat" maxOccurs="unbounded"
minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="voStandard" type="ApplicationCapability"
maxOccurs="unbounded"
minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="sourceLanguage" type="ProgrammingLanguage"
maxOccurs="unbounded"
minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="sourceCodeURL" type="xs:anyURI" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" />
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
| va:Application Extension Metadata Elements |
|---|
| Element | Definition |
|---|
| cost |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
an indication as to what the cost of the
application is - the string "free" or "none"
should be used to indicate that the application
does not cost anything. Any value for the cost
of any non-free software should be taken to be
an approximate cost for one license - it is
obviously difficult to curate this value for
non-free software so that the main use of this
element will be to distinguish between free and
non-free.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| licence |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
A free text value that indicates what type of
licence is in force. This can either be a common
name of a license or a URL pointing to the
license text.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| openSource |
| Value type: |
boolean (true/false): xs:boolean |
| Semantic Meaning: |
Is the software open source. See
http://www.opensource.org/docs/definition.php
for the definition of "open source"
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| dataFormat |
| Value type: |
DataFormat |
| Semantic Meaning: |
File formats that this application can read or
write. The formats are specified by reference to
an IVOA identifier that describes the format.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional; multiple occurrences allowed. |
|
| voStandard |
| Value type: |
ApplicationCapability |
| Semantic Meaning: |
enumerate which standards this application is
compliant with - *Editor note* not really too
happy with this, as there is a certain amount of
potential redundancy here if there is a derived
type - e.g. a CeaApplication type will support
CEA standard so at least one entry would have to
be placed here...
|
| Occurrences: |
optional; multiple occurrences allowed. |
|
| sourceLanguage |
| Value type: |
ProgrammingLanguage |
| Semantic Meaning: |
The IVOA identifier for the principal language
that the application is written in.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional; multiple occurrences allowed. |
|
| sourceCodeURL |
| Value type: |
a URI: xs:anyURI |
| Semantic Meaning: |
The location where the source code can be found.
This might be a URL to a specific archive file
containing the source, or to the access pages
for a source code management system.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
The IVOA identifiers to be used for the dataFormats and sourceLanguages are detailed in the section on Enumerations.
3.3. DesktopApplication
This is a concrete type that can be used to register real application that can be run on the user's desktop. In addition to the metadata described above, there is the possibility to add metadata for the following properties.
<xs:complexType name="DesktopApplication" >
<xs:complexContent >
<xs:extension base="Application" >
<xs:sequence >
<xs:element name="binarySize" type="xs:int" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="memoryRequirement" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1"
minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="network" type="NetworkRequirement" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="dependsOn" type="vr:IdentifierURI"
maxOccurs="unbounded"
minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="executable" type="ExecutionEnvironment"
maxOccurs="unbounded"
minOccurs="0" />
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
| va:DesktopApplication Extension Metadata Elements |
|---|
| Element | Definition |
|---|
| binarySize |
| Value type: |
|
| Semantic Meaning: |
The size of the executable in bytes.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| memoryRequirement |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
An estimate in bytes of the mimimum memory that
the application requires to function with
acceptable interactive performance.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| network |
| Value type: |
NetworkRequirement |
| Semantic Meaning: |
An assertion about the network requirements for
the proper functioning of the application.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
| Comments: |
This can take on the values;
- Essential
-
The application will not even start
without a network connection.
- Useful
-
The application will start, but the
primary use for the application requires a
network connection.
- Limited
-
The application makes only limited use of
network facilities, thus the majority of
its functionality is still available
without a network connection.
- Unnecessary
-
The application makes no use of the
network.
|
|
| dependsOn |
| Value type: |
an IVOA Identifier URI: vr:IdentifierURI |
| Semantic Meaning: |
Can be used to indicate other
applications/software libraries that the
application depends upon. This should only be
used to indicate dependencies that must be
installed separately from the main application
installation for it to function properly.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional; multiple occurrences allowed. |
|
| executable |
| Value type: |
ExecutionEnvironment |
| Semantic Meaning: |
how to obtain the executable
|
| Occurrences: |
optional; multiple occurrences allowed. |
|
binarySize
The size of the executable in bytes.
memoryRequirement
An estimate in bytes of the mimimum memory that the application requires to function with acceptable interactive performance.
network
An assertion about the network requirements for the proper functioning of the application. This can take on the values;
- Essential
- The application will not even start without a network connection.
- Useful
- The application will start, but the primary use for the application requires a network connection.
- Limited
- The application makes only limited use of network facilities, thus the majority of its functionality is still available without a network connection.
- Unnecessary
- The application makes no use of the network.
dependsOn
Can be used to indicate other applications/software libraries that the application depends upon. This should only be used to indicate depenedencies that must be installed separately from the application itself e.g. this element should not be used to indicate a dependency on a software library if the library is included in the application download.
executable
This is a complex type that is described further in the section on the ExecutionEnvionment type.
3.4. ExecutionEnvironment type
This type is intended to provide enough information for an executable image of the application to be downloaded and possibly automatically run. It should be noted of course that the automatic invocation of an application could possibly be dangerous and it only recommended for environments where a suitable "sandbox" is provided and/or cryptographic verification of the origin of the executable can be made.
<xs:complexType name="ExecutionEnvironment" >
<xs:sequence >
<xs:element name="platform" type="Platform" />
<xs:element name="architecture" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="subtype" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="minVersion" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="maxVersion" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" />
<xs:element name="download" type="xs:anyURI" maxOccurs="unbounded"
minOccurs="1" />
<xs:element name="path" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0" />
</sequence>
</complexType>
| va:ExecutionEnvironment Metadata Elements |
|---|
| Element | Definition |
|---|
| platform |
| Value type: |
Platform |
| Semantic Meaning: |
The major classification of the execution environment.
This should be an ivoa identifier for the platform
name;
|
| Occurrences: |
required |
|
| architecture |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
The hardware architecture that the software is
compiled for, if relevant.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| subtype |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
this is used to specify exactly the specific kind of
the environment - e.g. in the case of unix/linux it
would be nice if the output of uname would suffice
here - however the most common
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| minVersion |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
the minimum version of the environment that the code
will run in -
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| maxVersion |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
The highest version of the environment that this
applies to.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
| download |
| Value type: |
a URI: xs:anyURI |
| Semantic Meaning: |
The url that can be used to download (and possibly
execute) the application.
|
| Occurrences: |
required; multiple occurrences allowed. |
| Comments: |
This can actually point to different types of entity
depending on the platform e.g. for the "unix" platform
this would typically point to a compiled executable
image (though it might point to an archive or
"packaging" file that contains the executable amongst
other files). For the "Java Webstart" platform this
element will point to a ".jnlp" file that contains all
of the information necessary for the Java Webstart
technology to download and run the application.
|
|
| path |
| Value type: |
string: xs:string |
| Semantic Meaning: |
If the software image is packaged within some form of
archive format (e.g. tar or zip format) then this
element can be used to indicate the exact location of
the software image within the archive file.
|
| Occurrences: |
optional |
|
<!-- note that aladin can be started via webstart -->
<executable>
<platform>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#JavaWebStart
</platform>
<download>
http://aladin.u-strasbg.fr/java/nph-aladin.pl?frame=get&id=aladin.jnlp
</download>
</executable>
<!-- or downloaded directly-->
<executable>
<platform>ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Java</platform>
<download>
http://aladin.u-strasbg.fr/java/nph-aladin.pl?frame=get&id=Aladin.jar
</download>
</executable>
<!-- or even run as an applet -->
<executable>
<platform>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#JavaApplet
</platform>
<download>
http://aladin.u-strasbg.fr/java/nph-aladin.pl
</download>
</executable>
</ri:Resource>
3.5. SoftwareLibrary Type
The SoftwareLibrary type is used to register software that is not executable, but can be used as a component to build other executable software. The only metadata that the SoftwareLibrary type has beyond the basic Application type is that of the library element which is of type ExecutionEnvironment and can thus be used to indicate the location and platform that a library has been compiled for.
<xs:complexType name="SoftwareLibrary" >
<xs:complexContent >
<xs:extension base="Application" >
<xs:sequence >
<xs:element name="library" type="ExecutionEnvironment"
maxOccurs="unbounded"
minOccurs="1" >
</element>
</sequence>
</extension>
</complexContent>
</complexType>
| va:SoftwareLibrary Extension Metadata Elements |
|---|
| Element | Definition |
|---|
| library |
| Value type: |
ExecutionEnvironment |
| Semantic Meaning: |
|
| Occurrences: |
required; multiple occurrences allowed. |
|
3.6. Enumerations
In accordance with the guidelines laid down by [VR], there has been no attempt to create enumerated lists for cases where there list could not be closed (e.g. the set of operating system names will grow as new operating systems are developed). This means that the values of certain elements in a document instance will not be checked by even a validating XML parser, and validation that the element contents are allowed will have to be done by a separate process. This section will list the allowed values for those enumerations where appropriate and instance documents MUST use these exact strings to represent the same concept. These names are registered using the VOStandard schema [VSTD] as vstd:ResourceEnumList types, and the registry entries for the enumerations will be the definitive source for updates that occur after this document is published.
| | Type for which enum is valid | Value | Description |
|---|
| Programming languages | va:ProgrammingLanguage | ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#C | The C programming language - taken to include all variants of the language from K&R to ANSI. |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#CPP | The C++ programming language ISO/IEC 14882:1998 |
ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#CSharp | The C# programming language http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/files/ECMA-ST/Ecma-334.pdf |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#FORTRAN | The FORTRAN programming language - Includes all versions of the language |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#Java | The Java programming language http://java.sun.com/ |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#Perl | The Perl programming language http://www.perl.org/ |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#Python | The Python programming language http://www.python.org/ |
| Data Formats | va:DataFormat | ivo://net.ivoa.application/formats#FITS | The FITS data format http://fits.gsfc.nasa.gov/documents.html |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/formats#VOTable | The VOTable format [VOTable] |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/formats#HDF | http://www.hdfgroup.org/ |
| Execution Environments | va:Platform | ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Unix | This includes all variations, as well as Linux |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Windows | All varieties of Microsoft Windows |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#JavaWebStart | A Java application that can be launched using the WebStart mechanism |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#JavaApplet | A Java executable that can be launched as an applet |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Perl | � |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Python | � |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#IRAF | � |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#PyRaf | ?? |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#IDL | � |
| ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#OSX | Apple OS X |
The procedure to add to these enumerations is to apply by email to the curators of the respective resources
4. Examples of use of the Application Schema
1. Common Execution Architecture (CEA)
The VOCEA schema that is used to register CEA information [CEADM] is a good example of how the VOApplication schema can be extended. This has already been illustrated in the UML diagram earlier in this document.
1. SAMP
TBC
Appendix A. The complete VOApplication
Schema
Note that this schema can be found on-line at http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOApplication/v1.0 (i.e. the target namespace
can also be used as a URL for the schema.) This location should
represent the definitive source, the schema is only copied below for
completeness of this document.
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOApplication/v1.0rc1" elementFormDefault="unqualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified" version="1.0 $Revision: 1.3.2.2 $" xmlns:xml="http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace" xmlns:="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOApplication/v1.0rc1" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:vr="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOResource/v1.0" xmlns:vm="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOMetadata/v0.1"><xs:import schemaLocation="../../VOResource/v1.0/VOResource.xsd" namespace="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOResource/v1.0"/>
<xs:annotation><xs:appinfo><vm:schemaName>VOApplication</vm:schemaName>
<vm:schemaPrefix>xs</vm:schemaPrefix>
<vm:targetPrefix>va</vm:targetPrefix>
</xs:appinfo> <xs:documentation>
This is a schema for describing applications.. See complete
specification at
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/latest/VOApplication.html.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:complexType name="Application"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The basic description of an application.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:complexContent><xs:extension base="vr:Resource"><xs:sequence><xs:element name="cost" minOccurs="0" type="xs:string"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
an indication as to what the cost of the
application is - the string "free" or "none"
should be used to indicate that the application
does not cost anything. Any value for the cost
of any non-free software should be taken to be
an approximate cost for one license - it is
obviously difficult to curate this value for
non-free software so that the main use of this
element will be to distinguish between free and
non-free.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="licence" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
A free text value that indicates what type of
licence is in force. This can either be a common
name of a license or a URL pointing to the
license text.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="openSource" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
Is the software open source. See
http://www.opensource.org/docs/definition.php
for the definition of "open source"
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="dataFormat" type="DataFormat" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
File formats that this application can read or
write. The formats are specified by reference to
an IVOA identifier that describes the format.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="voStandard" type="ApplicationCapability" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
enumerate which standards this application is
compliant with - *Editor note* not really too
happy with this, as there is a certain amount of
potential redundancy here if there is a derived
type - e.g. a CeaApplication type will support
CEA standard so at least one entry would have to
be placed here...
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="sourceLanguage" type="ProgrammingLanguage" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The IVOA identifier for the principal language
that the application is written in.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="sourceCodeURL" type="xs:anyURI" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The location where the source code can be found.
This might be a URL to a specific archive file
containing the source, or to the access pages
for a source code management system.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> </xs:sequence> </xs:extension> </xs:complexContent> </xs:complexType> <xs:complexType name="DesktopApplication"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
An application that can actually be run on a user's desktop
computer.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:complexContent><xs:extension base="Application"><xs:sequence><xs:element name="binarySize" type="xs:int" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The size of the executable in bytes.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="memoryRequirement" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
An estimate in bytes of the mimimum memory that
the application requires to function with
acceptable interactive performance.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="network" type="NetworkRequirement" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
An assertion about the network requirements for
the proper functioning of the application.
</xs:documentation>
<xs:documentation>
This can take on the values;
<dl><dt>Essential</dt>
<dd>
The application will not even start
without a network connection.
</dd>
<dt>Useful</dt>
<dd>
The application will start, but the
primary use for the application requires a
network connection.
</dd>
<dt>Limited</dt>
<dd>
The application makes only limited use of
network facilities, thus the majority of
its functionality is still available
without a network connection.
</dd>
<dt>Unnecessary</dt>
<dd>
The application makes no use of the
network.
</dd>
</dl> </xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="dependsOn" type="vr:IdentifierURI" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
Can be used to indicate other
applications/software libraries that the
application depends upon. This should only be
used to indicate dependencies that must be
installed separately from the main application
installation for it to function properly.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="executable" type="ExecutionEnvironment" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
how to obtain the executable
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> </xs:sequence> </xs:extension> </xs:complexContent> </xs:complexType> <xs:complexType name="SoftwareLibrary"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
Software the cannot be independently executed, but can be
used to build applications
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:complexContent><xs:extension base="Application"><xs:sequence><xs:element name="library" type="ExecutionEnvironment" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1">
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence> </xs:extension> </xs:complexContent> </xs:complexType> <xs:complexType name="ExecutionEnvironment"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
Description of the full execution environment. Where
possible this description should be sufficient to download
and run the application.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:sequence><xs:element name="platform" type="Platform"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The major classification of the execution environment.
This should be an ivoa identifier for the platform
name;
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="architecture" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The hardware architecture that the software is
compiled for, if relevant.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="subtype" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
this is used to specify exactly the specific kind of
the environment - e.g. in the case of unix/linux it
would be nice if the output of uname would suffice
here - however the most common
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="minVersion" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
the minimum version of the environment that the code
will run in -
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="maxVersion" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The highest version of the environment that this
applies to.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="download" type="xs:anyURI" maxOccurs="unbounded" minOccurs="1"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The url that can be used to download (and possibly
execute) the application.
</xs:documentation>
<xs:documentation>
This can actually point to different types of entity
depending on the platform e.g. for the "unix" platform
this would typically point to a compiled executable
image (though it might point to an archive or
"packaging" file that contains the executable amongst
other files). For the "Java Webstart" platform this
element will point to a ".jnlp" file that contains all
of the information necessary for the Java Webstart
technology to download and run the application.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> <xs:element name="path" type="xs:string" maxOccurs="1" minOccurs="0"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
If the software image is packaged within some form of
archive format (e.g. tar or zip format) then this
element can be used to indicate the exact location of
the software image within the archive file.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:element> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> <xs:complexType name="DataFormat"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
Data File Format. This should be a uri reference to a value
from the ivo://net.ivoa.application/formats resource. Editor
note - it would really be nice to have a connection with
mime-types here rather/as well as the standard reference
mechanism
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:attribute name="standardID" type="xs:anyURI" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="direction" type="DataFormatDirection" use="required">
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType> <xs:simpleType name="ProgrammingLanguage"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The programming language. This should be a uri reference to
a value from the ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages
resource.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:restriction base="xs:anyURI">
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType> <xs:simpleType name="Platform"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The execution environment name. This should be a uri
reference to a value from the
ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms resource.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:restriction base="xs:anyURI">
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType> <xs:complexType name="ApplicationCapability"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
generic description of a capability of an application - this
is different from a service capability because it does not
have an interface associated - perhaps should be derived
from a common base class though.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:attribute name="standardID" type="vr:IdentifierURI"/>
</xs:complexType> <xs:simpleType name="NetworkRequirement"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
Characterization as to whether a network connection is
required by the application.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:restriction base="xs:string"><xs:enumeration value="Essential"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The application cannot function without a network
connection
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:enumeration> <xs:enumeration value="Useful"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The application will function without a network
connection, but the primary use for the application
requires a network connection.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:enumeration> <xs:enumeration value="Limited"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The application makes only limited use of network
facilities, thus the majority of its functionality is
still available without a network connection.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:enumeration> <xs:enumeration value="Unnecessary"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
The application makes no use of the network.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> </xs:enumeration> </xs:restriction> </xs:simpleType> <xs:simpleType name="DataFormatDirection"><xs:annotation><xs:documentation>
Description of whether an application can both read and
write a particular data format.
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation> <xs:restriction base="xs:string"><xs:enumeration value="read"/>
<xs:enumeration value="write"/>
<xs:enumeration value="both"/>
</xs:restriction> </xs:simpleType> </xs:schema>
Appendix B. The complete source of the
examples presented
The example instances of the the VOApplication schema show
several features of how to use the schema to register applications.
<ri:VOResources xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/RegistryInterface/v1.0 http://www.ivoa.net/xml/RegistryInterface/v1.0 http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOApplication/v1.0rc1 VOApplication.xsd" from="1" more="false" numberReturned="4" xmlns:xml="http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace" xmlns:ri="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/RegistryInterface/v1.0" xmlns:app="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOApplication/v1.0rc1" xmlns:vr="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOResource/v1.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"><ri:Resource updated="2006-08-13T00:00:00" created="2006-08-13T00:00:00" status="active" xsi:type="app:DesktopApplication"><title>The Aladin Sky Atlas</title>
<shortName>Aladin</shortName>
<identifier>ivo://cds.fr/applications/aladin</identifier>
<curation><publisher ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">String</publisher>
<creator><name ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">Centre des Données Astronomiques de Strasbourg</name>
<logo>http://cdsweb.u-strasbg.fr/Icons/cds_icon.gif</logo>
</creator> <date role="representative">1967-08-13</date>
<version>String</version>
<contact><name ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">Pierre Fernique</name>
<address>String</address>
<email>String</email>
<telephone>String</telephone>
</contact> </curation> <content><subject>String</subject>
<description>Aladin is an interactive software sky atlas allowing the user to visualize digitized images of any part of the sky, to superimpose entries from astronomical catalogs or personal user data files, and to interactively access related data and information from the SIMBAD, NED, VizieR, or other archives for all known objects in the field. Aladin is particularly useful for multi-spectral cross-identifications of astronomical sources, observation preparation and quality control of new data sets.</description>
<referenceURL>http://aladin.u-strasbg.fr/</referenceURL>
<type>Other</type>
<contentLevel>General</contentLevel>
</content> <dataFormat standardID="ivo://net.ivoa.application/formats#FITS" direction="both"/>
<dataFormat standardID="ivo://net.ivoa.application/formats#VOtable" direction="both"/>
<voStandard standardID="ivo://ivoa.net/SIA"/>
<sourceLanguage>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/language#Java
</sourceLanguage>
<executable><platform>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#JavaWebStart
</platform>
<download>
http://aladin.u-strasbg.fr/java/nph-aladin.pl?frame=get&id=aladin.jnlp
</download>
</executable> <executable><platform>ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Java</platform>
<download>
http://aladin.u-strasbg.fr/java/nph-aladin.pl?frame=get&id=Aladin.jar
</download>
</executable> <executable><platform>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#JavaApplet
</platform>
<download>
http://aladin.u-strasbg.fr/java/nph-aladin.pl
</download>
</executable> </ri:Resource> <ri:Resource updated="1967-08-13T00:00:00" created="1967-08-13T00:00:00" status="active" xsi:type="app:DesktopApplication"><title>The AstroGrid Workbench</title>
<shortName>Workbench</shortName>
<identifier>
ivo://org.astrogrid/applications/workbench
</identifier>
<curation><publisher ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">String</publisher>
<creator><name ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">String</name>
<logo>http://www.ivoa.net/pub/images/IVOA_wb_300.jpg</logo>
</creator> <contributor ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">String</contributor>
<date role="representative">1967-08-13</date>
<version>1.3</version>
<contact><name>Noel Winstanley</name>
<address>Astrogrid</address>
<email>nw@jb.man.ac.uk</email>
</contact> </curation> <content><subject>Astrogrid Workbench</subject>
<description>
The Workbench is a graphical desktop application that
interacts with AstroGrid services. It provides a user
interface to Browse, read and write MySpace Launch
Parameterized Workflows Launch remote (CEA) applications
Monitor and control workflows and applications View registry
entries a simple programmer's interface for working with
AstroGrid services. This interface can be accessed from
scripts and other programs via HTTP, XMLRPC or JavaRMI
</description>
<source format="String">String</source>
<referenceURL>
http://software.astrogrid.org/userdocs/workbench.html
</referenceURL>
<type>Other</type>
<contentLevel>General</contentLevel>
<relationship><relationshipType>mirror-of</relationshipType>
<relatedResource ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">
String
</relatedResource>
<relatedResource ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">
String
</relatedResource>
</relationship> </content> <licence>Academic Free</licence>
<openSource>true</openSource>
<sourceLanguage>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/language#Java
</sourceLanguage>
<executable><platform>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#JavaWebStart
</platform>
<minVersion>1.4</minVersion>
<download>
http://software.astrogrid.org/jnlp/astrogrid-desktop/astrogrid-desktop.jnlp
</download>
</executable> </ri:Resource> <ri:Resource updated="1967-08-13T00:00:00" created="1967-08-13T00:00:00" status="active" xsi:type="app:SoftwareLibrary"><title>Starlink Tables Infrastructure Library</title>
<shortName>STIL</shortName>
<identifier>ivo://starlink.org/applications/stil</identifier>
<curation><publisher ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">String</publisher>
<creator><name ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">String</name>
<logo>http://www.ivoa.net/pub/images/IVOA_wb_300.jpg</logo>
</creator> <contributor ivo-id="ivo://xxx/x/x">String</contributor>
<date role="representative">1967-08-13</date>
<version>2.3-1</version>
<contact><name>Mark Taylor</name>
<address>Starlink</address>
<email>m.b.taylor@bristol.ac.uk</email>
</contact> </curation> <content><subject>
STIL - Starlink Tables Infrastructure Library
</subject>
<description>
STIL is a pure Java library for generic input, output and
processing of tabular data. It presents to the application
programmer a view of a table which looks the same regardless
of whether it came from a FITS file, a VOTable, an ASCII
text file, a query on a relational database, or whatever.
Thus the application doesn't have to worry about the storage
format of tables either when reading or writing them, it can
concentrate on doing processing. STIL's idea of a table is
rich enough to include table and column metadata, and table
cells which contain scalar or single- or multi-dimensional
array data of numerical, string or other types. This is well
suited to astronomical data, though it can be of use in
other fields as well.
</description>
<source format="String">String</source>
<referenceURL>
http://www.star.bristol.ac.uk/~mbt/stil/
</referenceURL>
<type>Other</type>
<contentLevel>General</contentLevel>
</content> <sourceLanguage>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/language#Java
</sourceLanguage>
<library><platform>ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Java</platform>
<minVersion>1.4</minVersion>
<download>
http://www.star.bristol.ac.uk/~mbt/stil/stil.jar
</download>
</library> </ri:Resource> <ri:Resource xsi:type="app:DesktopApplication" updated="1967-08-13T00:00:00" created="1967-08-13T00:00:00" status="active"><title>SExtractor</title>
<shortName>SExtractor</shortName>
<identifier>ivo://org.astrogrid/apps/SExtractor</identifier>
<curation><publisher>Astrogrid</publisher>
<creator><name>Terapix</name>
<logo>http://terapix.iap.fr/IMG/terapix.png</logo>
</creator> <date role="representative">2004-03-26</date>
<version>2.5.0</version>
<contact><name>Paul Harrison</name>
<email>pah@jb.man.ac.uk</email>
</contact> </curation> <content><subject>???</subject>
<description>
SExtractor is a program that builds a catalogue of objects
from an astronomical image. Although it is particularly
oriented towards reduction of large scale galaxy-survey
data, it performs rather well on moderately crowded star
fields.
</description>
<referenceURL>
http://terapix.iap.fr/cplt/oldSite/soft/sextractor/
</referenceURL>
<type>Other</type>
</content> <cost>free</cost>
<sourceLanguage>
ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages#C
</sourceLanguage>
<sourceCodeURL>
ftp://ftp.iap.fr/pub/from_users/bertin/sextractor/sextractor-2.5.0.tar.gz
</sourceCodeURL>
<executable><platform>ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms#Unix</platform>
<architecture>x86</architecture>
<download>
ftp://ftp.iap.fr/pub/from_users/bertin/sextractor/sextractor-2.5.0-1.i686.rpm
</download>
</executable> </ri:Resource> </ri:VOResources>
Appendix C. The complete source of the
enumerations presented
The source below shows how the enumerations are defined as resources using the VOStandard schema
<p:VOResources xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/RegistryInterface/v1.0 http://www.ivoa.net/xml/RegistryInterface/v1.0 http://www.ivoa.net/xml/StandardsRegExt/v1.0 /Users/pharriso/Work/ag/src/contracts/src/schema/vo-resource-types/VOStandard/v1.0/VOStandard.xsd http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOResource/v1.0 http://www.ivoa.net/xml/VOResource/v1.0 " from="1" more="false" numberReturned="3" xmlns:xml="http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace" xmlns:p="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/RegistryInterface/v1.0" xmlns:vstd="http://www.ivoa.net/xml/StandardsRegExt/v1.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"><p:Resource xsi:type="vstd:StandardKeyEnumeration" created="2001-12-31T12:00:00" updated="2001-12-31T12:00:00" status="active"><title>application languages</title>
<identifier>ivo://net.ivoa.application/languages</identifier>
<curation><publisher>IVOA</publisher>
<creator><name>IVOA</name>
<logo>http://www.ivoa.net/icons/ivoa_logo_small.jpg</logo>
</creator> <date role="representative">2006-07-17</date>
<version>1.0</version>
<contact><name>IVOA Grid Registry WG</name>
<email>registry@ivoa.net</email>
</contact> </curation> <content><subject>standard language identifiers</subject>
<description>These language identifiers are to be used in
the value of the va:ProgrammingLanguage type</description>
<referenceURL>
http://www.ivoa.net/twiki/bin/view/IVOA/IvoaResReg</referenceURL>
</content> <key><name>C</name>
<description>The C programming language</description>
</key> <key><name>CPP</name>
<description>The C++ programming language</description>
</key> <key><name>CSharp</name>
<description>The C# programming language</description>
</key> <key><name>FORTRAN</name>
<description>The FORTRAN programming language</description>
</key> <key><name>Java</name>
<description>The Java programming language</description>
</key> <key><name>Perl</name>
<description>The Perl programming language</description>
</key> <key><name>Python</name>
<description>The Python programming language</description>
</key> </p:Resource> <p:Resource xsi:type="vstd:StandardKeyEnumeration" created="2001-12-31T12:00:00" updated="2001-12-31T12:00:00" status="active"><title>application data formats</title>
<identifier>ivo://net.ivoa.application/formats</identifier>
<curation><publisher>IVOA</publisher>
<creator><name>IVOA</name>
<logo>http://www.ivoa.net/icons/ivoa_logo_small.jpg</logo>
</creator> <date role="representative">2006-07-17</date>
<version>1.0</version>
<contact><name>IVOA Grid Registry WG</name>
<email>registry@ivoa.net</email>
</contact> </curation> <content><subject>standard language identifiers</subject>
<description>These data format identifiers are to be used in
the value of the va:DataFormat type</description>
<referenceURL>
http://www.ivoa.net/twiki/bin/view/IVOA/IvoaResReg</referenceURL>
</content> <key><name>FITS</name>
<description>The FITS data format</description>
</key> <key><name>HDF</name>
<description>The HDF data format</description>
</key> <key><name>VOTable</name>
<description>The FITS data format</description>
</key> </p:Resource> <p:Resource xsi:type="vstd:StandardKeyEnumeration" created="2001-12-31T12:00:00" updated="2001-12-31T12:00:00" status="active"><title>application execution environments</title>
<identifier>ivo://net.ivoa.application/platforms</identifier>
<curation><publisher>IVOA</publisher>
<creator><name>IVOA</name>
<logo>http://www.ivoa.net/icons/ivoa_logo_small.jpg</logo>
</creator> <date role="representative">2006-07-17</date>
<version>1.0</version>
<contact><name>IVOA Grid Registry WG</name>
<email>registry@ivoa.net</email>
</contact> </curation> <content><subject>standard execution environment identifiers</subject>
<description>These execution environment identifiers are
to be used in the value of the va:Platform type</description>
<referenceURL>
http://www.ivoa.net/twiki/bin/view/IVOA/IvoaResReg</referenceURL>
</content> <key><name>Unix</name>
<description>One of the Unix/Linux operating systems</description>
</key> <key><name>Windows</name>
<description>One of the Microsoft Windows operating systems</description>
</key> <key><name>JavaWebStart</name>
<description>Downloadable and executable via the
Java Web Start technology</description>
</key> <key><name>JavaApplet</name>
<description>Downloadable and executable via the
Java Applet technology</description>
</key> <key><name>Perl</name>
<description>A script or module that executes under Perl</description>
</key> <key><name>Python</name>
<description>A script or module that executes under Python</description>
</key> <key><name>IRAF</name>
<description>A script or module that executes under IRAF</description>
</key> <key><name>PyRaf</name>
<description>A script or module that executes under PyRaf</description>
</key> <key><name>IDL</name>
<description>A script or module that executes under IDL</description>
</key> </p:Resource> </p:VOResources>
Appendix D. Change History
This is the first version that has been made public - it is
derived from wiki content.
- [RFC 2119]
- Bradner, S. 1997.
[]
, IETF RFC 2119,
http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt - [RM]
- Hanisch, Robert (ed.) 2004.
[]
, IVOA Recommendation,
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/REC/ResMetadata/RM-20040426.htm - [VR]
- Plante, Ray (ed.) 2006. VOResource: an XML Encoding Schema for Resource Metadata, IVOA Working Draft,
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/latest/VOResource.html - [VSTD]
- Harrison, Paul. (ed.) 2006. VOStandard: an XML Encoding Schema for IVOA Standards, IVOA Working Draft,
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/latest/VOResource.html - [CEA]
- Harrison, Paul. 2006. A Proposal for a Common Execution Architecture , IVOA Working Draft,
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/latest/VOCEA.html -
- [CEADM]
- Harrison, Paul. 2007. CEA Application Model: A model and XML Encoding Schema for Applications in the Common Execution Architecture, IVOA Working Draft,
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/latest/CEADM.html -
-
[xml]
- Bray, Tim, Paoli, Jean, Sperberg-McQueen, C. M., Maler, Eve,
Yergeau, Francois (editors) 2004,
[]
, W3C Recommendation
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml
- [schema]
- Fallside, David C., Walmsley, Priscilla (editors) 2004,
[]
, W3C Recommendation 28
October 2004,
http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-0/
- [ID]
- Plante, R., Linde, T., Williams, R., Noddle, K. 2005,
[]
,
http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/REC/Identifiers/Identifiers-200505XX.html.
- ï
$Revision: 847 $ $Date: 2008-10-29 14:33:57 +0000 (Wed, 29. Oct 2008) $

