| 1. | model: IVOA Profile |
| 2. | Packages and Types |
| 2.1 | [root package] |
| 2.2 | package: stdtypes |
| 2.2.1 | dataType: Identity |
| 2.2.2 | primitiveType: anyURI |
| 2.2.3 | primitiveType: boolean |
| 2.2.4 | primitiveType: complex |
| 2.2.5 | primitiveType: datetime |
| 2.2.6 | primitiveType: decimal |
| 2.2.7 | primitiveType: duration |
| 2.2.8 | primitiveType: integer |
| 2.2.9 | primitiveType: nonnegativeInteger |
| 2.2.10 | primitiveType: rational |
| 2.2.11 | primitiveType: real |
| 2.2.12 | primitiveType: string |
| 3. | UTYPE-s |
| 4. | Path Expressions-s |
| Authors | : | |
| Date | : | 2013-03-24T06:58:05 |
| Version | : | 0.x |
| Abstract | : | This is the main reference data model containing primitive types used in other data models. |
| Diagram | : | The following diagram has been generated from the model using the GraphViz tool. The classes and packages in the diagram can be clicked and are mapped to the descriptions of the corresponding element elsewhere in the document. |
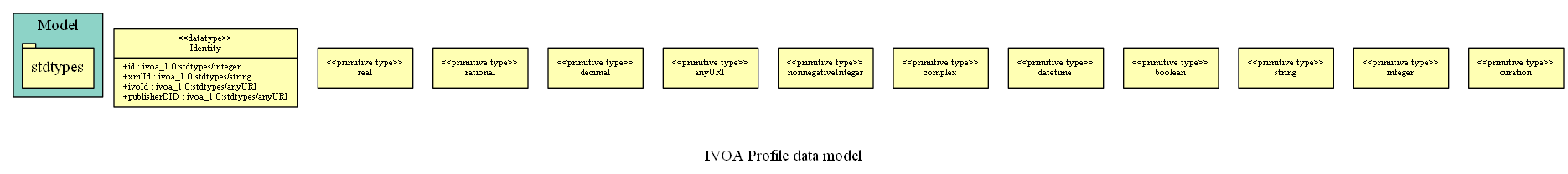
The following sub-sections present all packages in the model with their types. The packages are listed here in alphabetical order. Each sub-section contains a description of the package and a table containing its various features.
| Model | ivoa_1.0 | |
| child package(s) | stdtypes | |
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/ | |
| description | TODO : Missing description : please, update your UML model asap. | |
| parent | IVOA Profile | |
| Data types | Identity | |
| Primitive types | anyURI boolean complex datetime decimal duration integer nonnegativeInteger rational real string | |
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| description | This datatype represents an identifier for an object in the data model. It consists of 3 attributes that each are assumed to work in a particular context or representation of a data model instance. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/anyURI | ||
| description | Represents a URI in the same way as the datatype of the same nam in XML Schema is used. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/boolean | ||
| description | The standard boolean, having values true or false. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/complex | ||
| description | Represents a complex number, consisting of a real and imaginary component, both of which are reals. Note that in many contexts there is no native mapping for this type and it must be treated with a custom mapping. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/datetime | ||
| description | Represents a moment in time using a date+timestamp. Coordinate reference systems must be defined by the context serialisation. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/decimal | ||
| description | Represents a decimal number with exact significance such as used to denote monetary values. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/duration | ||
| description | Represents an interval of time from beginning to end. Is not equivalent to a simple real value indicating the number of seconds (for example). In general a custom mapping to a particular serialisation context must be provided. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/integer | ||
| description | An integer number (from Z). | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/nonnegativeInteger | ||
| description | An integer number from N, therefore greater than or equal to 0. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/rational | ||
| description | A rational number from Q, represented by two integers, a numerator and a denominator. A native mapping to a serialisation context does in general not exists. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/real | ||
| description | A real number (from R). | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| utype | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/string | ||
| description | A string, represented as an array of characters treated as a single, primitive value. Ala Java, a string can not be updated, that is any update leads to a different string. However in contrast to Java we assume that two strings that are identical in all their constitutent characters are the same. I.e. string has value type semantics. | ||
| package | stdtypes | ||
| UTYPE | feature type | description |
| ivoa_1.0 | vo-dml:model | This is the main reference data model containing primitive types used in other data models. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/ | package | TODO : Missing description : please, update your UML model asap. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity | dataType | This datatype represents an identifier for an object in the data model. It consists of 3 attributes that each are assumed to work in a particular context or representation of a data model instance. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.id | attribute | The id attribute is assumed to represent an object in a database storing instances of the data model. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.ivoId | attribute | The ivoId attribute is assumed to represent an object in a database following the design of the data model and accessible through a standardised registration and discovery protocols. It is assumed to be unique within the IVOA and its format follows (a generalisation of) the IVO Resource Identifier standard (see http://www.ivoa.net/Documents/REC/Identifiers/Identifiers-20070302.html). Since the ivoId is assumed to represent the resource as registered in a standard database for the data model, it is assumed to be allocated by such a database service. This is in contrast to the use of the IVO Identifier in resource registries, where the id is assumed to be allocated by the publisher. We have the publisherDID attribute for that purpose. Also in contrast to that usage is the fact that each object in the model is assigned this identifier, not only the root resources. We suggest as algorithm for assigning these ivoId to use as root the ivoId of the registered database service, and to append to this a # then the UTYPE of the element and finally its id attribute, separetd from the UTYPE by a forward slash. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.publisherDID | attribute | This attribute identifies an element in the context of the publisher. It is supposed to be unique in the IVO context and should likely be constrained to have the publisher's authority IVO id. This may need to be rediscussed when protocols for accessing a database built around a data model are to be designed. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.xmlId | attribute | This attribute is used to support identifing of and referring to an object in an XML document using the ID/IDREF mechanism. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/anyURI | primitiveType | Represents a URI in the same way as the datatype of the same nam in XML Schema is used. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/boolean | primitiveType | The standard boolean, having values true or false. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/complex | primitiveType | Represents a complex number, consisting of a real and imaginary component, both of which are reals. Note that in many contexts there is no native mapping for this type and it must be treated with a custom mapping. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/datetime | primitiveType | Represents a moment in time using a date+timestamp. Coordinate reference systems must be defined by the context serialisation. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/decimal | primitiveType | Represents a decimal number with exact significance such as used to denote monetary values. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/duration | primitiveType | Represents an interval of time from beginning to end. Is not equivalent to a simple real value indicating the number of seconds (for example). In general a custom mapping to a particular serialisation context must be provided. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/integer | primitiveType | An integer number (from Z). |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/nonnegativeInteger | primitiveType | An integer number from N, therefore greater than or equal to 0. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/rational | primitiveType | A rational number from Q, represented by two integers, a numerator and a denominator. A native mapping to a serialisation context does in general not exists. |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/real | primitiveType | A real number (from R). |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/string | primitiveType | A string, represented as an array of characters treated as a single, primitive value. Ala Java, a string can not be updated, that is any update leads to a different string. However in contrast to Java we assume that two strings that are identical in all their constitutent characters are the same. I.e. string has value type semantics. |
| PATH | Linked PATH | Corresopnding UTYPE path |
| ivoa_1.0 | ivoa_1.0 | ivoa_1.0 |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes | ivoa_1.0/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/ |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity | ivoa_1.0/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes//ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.id | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.id | ivoa_1.0/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes//ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.id |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.xmlId | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.xmlId | ivoa_1.0/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes//ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.xmlId |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.ivoId | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.ivoId | ivoa_1.0/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes//ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.ivoId |
| ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.publisherDID | ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.publisherDID | ivoa_1.0/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes//ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity/ivoa_1.0:stdtypes/Identity.publisherDID |